How big is WorldView-4?
Big. About the size of the Chevy Suburban, excluding the solar arrays. But why is it so big? The satellite’s telescope accounts for more than two thirds of its total size. While modern electronics have decreased the size and cost of satellite components like onboard processors, radios, and digital storage, there is no way to reduce the size of the telescope without degrading the resolution of its images, simply due to the laws of physics. Our customers need high-resolution images, so our satellites need large telescopes.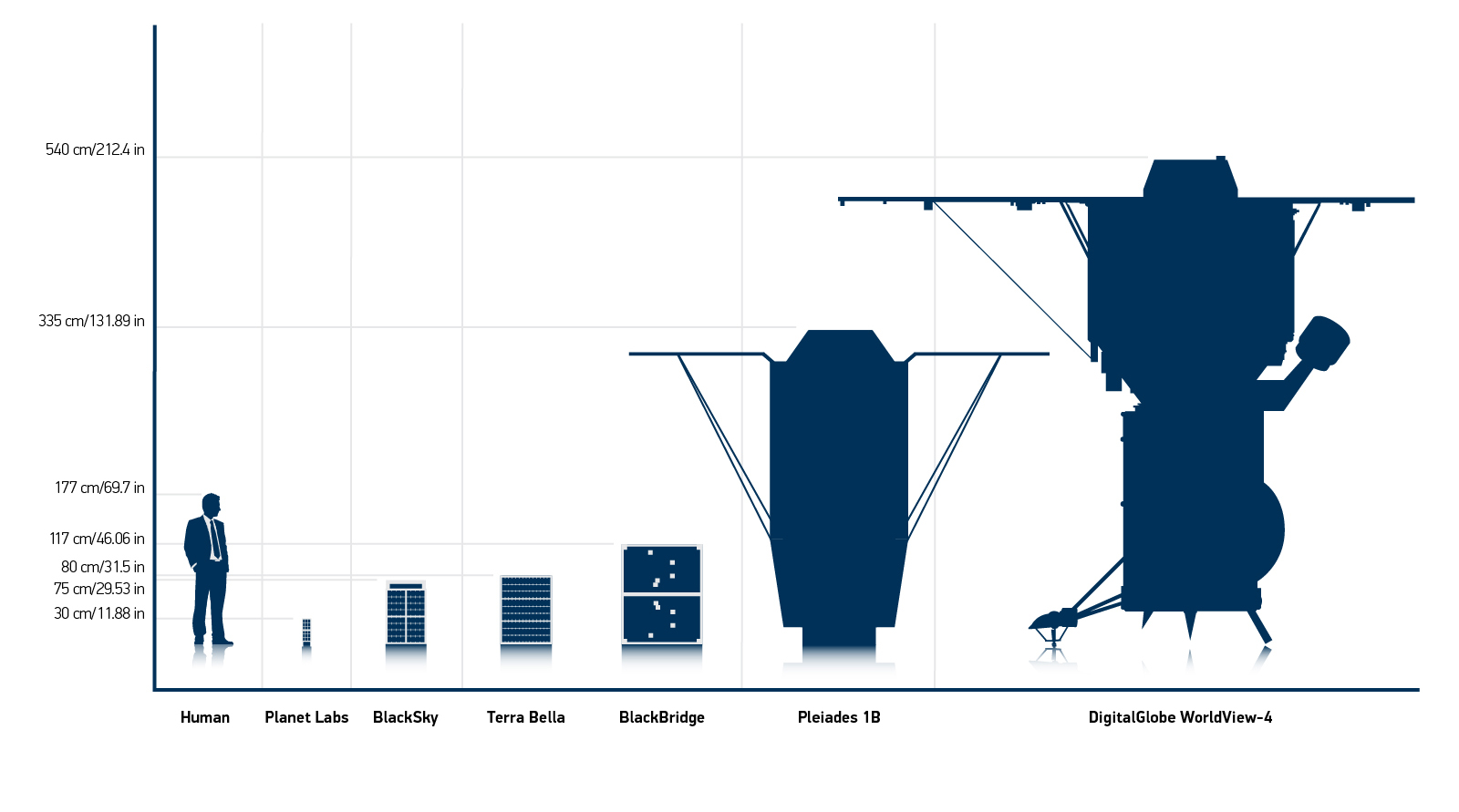
Does WorldView-4 have a pilot, like a plane?
You can imagine that with a satellite constellation that will, with WorldView-4, collect north of 4 million square kilometers of the earth imagery every day—and with a global network of a dozen ground stations to manage communicating with this constellation, things could get rather hectic. Fortunately, we have a highly automated planning system that takes into account a multitude of factors (including satellite positions, weather, customer orders, and targets of opportunity) to build a continuously updated “mission plan” to fly the satellites. This all happens in the background, which lets us manage this entire process with a small handful of highly-trained satellite operators whose job it is to make sure this automated system keeps working the way it should, and to manage the very infrequent situations where things do not. This combination of person and machine is what lets us operate 365/24/7 and maintain a satellite collection uptime of 99.7-99.9%.How does WorldView-4 know exactly where it is, and what it’s looking at?
WorldView-4 carries a GPS receiver that tells it where it is, just like the GPS receiver in your car tells you where you are. In addition, WorldView-4 carries a pair of “star trackers” – cameras that look up at the sky – which tell it where its telescope is pointed. The combination of satellite position (from GPS) and satellite “attitude” (orientation, from the star trackers) lets us know exactly where the telescope is looking on the ground to a staggering degree of accuracy – off by less than the distance from a basketball rim to the free throw line, from hundreds of miles away.Can WorldView-4’s telescope focus on different things?
Absolutely! While WorldView-4 is pointed at the ground, it isn’t always pointed straight down at what is directly below. Rather, it can pivot around to capture the images that are of interest to our customers. This means that it may look forward, or back, or left, or right, and maneuver in between. To do this, it uses a technology called “control moment gyros,” which work in much the same way to move WorldView-4 as the spinning bicycle wheel does to move the man on the stool in this YouTube video. In fact, because of its large telescope and ability to pivot, WorldView-4 is able to take images at a wide range of angles and distances and still collect super-sharp images. Here’s what the Las Vegas Strip looks like when one of our satellites images it from almost directly overhead, and below that, what it looks like when a satellite is 1,770 kilometers west of the city and tilted 63.7 degrees off-nadir. Your browser does not support iframe, click here for full map [caption id="attachment_4846" align="alignnone" width="800"]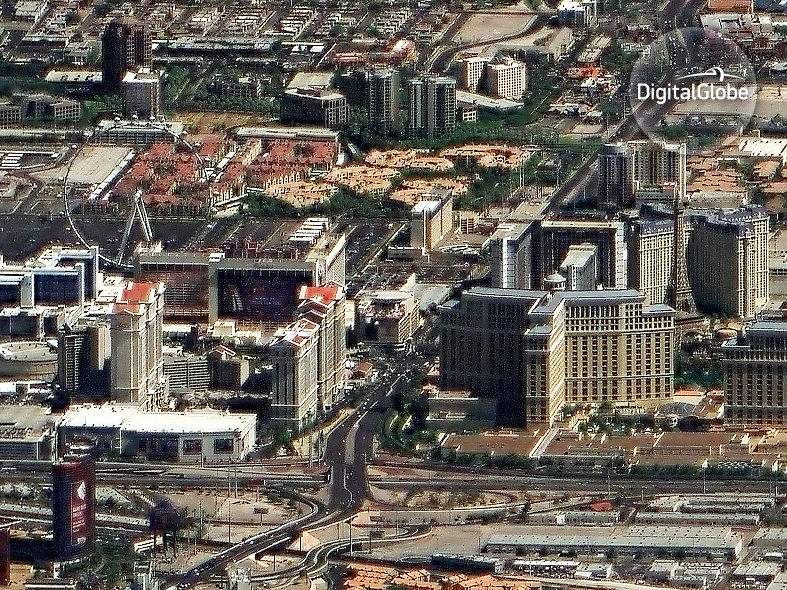 Click here to see the entire Las Vegas strip.[/caption]
Click here to see the entire Las Vegas strip.[/caption]
How do WorldView-4 images get back to earth?
WorldView-4 sends images back the ground using radio, much as your mobile device communicates with a Wi-Fi router. The only difference is that while you might be 200 feet away from your Wi-Fi router, WorldView-4 does this from several hundred miles straight up and several thousand miles off to the side, yet it is blasting this data to the ground at a speed that is roughly as fast as the fastest Wi-Fi! Since WorldView-4 can be over nearly any part of the planet as it orbits around the earth, we have put in place a network of a dozen “remote ground terminals” with big dishes and radio gear to capture the data from WorldView-4 and then relay it back to DigitalGlobe.Can DigitalGlobe satellites take an image of every place on earth each day?
On the one hand, the DigitalGlobe constellation can revisit (meaning be in a position from which it could take a picture if desired) any place on the planet three or four times or more every day. So if there were a particularly interesting location that warranted being visited this often—such as the immediate aftermath of a natural disaster like this spring’s Fort McMurray wildfires, the DigitalGlobe constellation can address it. However, there is a difference between being able to image anywhere on earth at least daily and being able to image everywhere on the earth at least daily. The earth’s surface area is roughly 510 million square kilometers. The DigitalGlobe constellation can collect 4 million square kilometers every day, which means that it could theoretically image the earth’s entire surface in about four months. But how much of that area is of interest to customers? First, let’s rule out the largely empty oceans and seas, which cover 71% of the surface of the earth, and also Antarctica (interesting for penguins but not so much for people), leaving about 150 million square kilometers of land. Next, let’s exclude the 60% or so of earth’s landmass that is covered by clouds on any given day. Now we’re down to about 60 million square kilometers of cloud-free, observable land area. If we consider that 95% of the world’s population lives on just 10% of the earth’s landmass, then we can infer that a great proportion of the most interesting activities on earth are actually taking place on a tiny sliver of its surface. In essence, this is the reason we build large, steerable satellites: to collect as much information as possible, as frequently as possible, about the most interesting and dynamic places on earth. The visualization below shows how frequently we’ve imaged each part of the planet over the past 16 years; you can see the vast difference in the collections of highly populated coastal areas and cities compared to the world’s oceans, deserts, and arctic regions. And because the DigitalGlobe constellation is the highest resolution in the industry, this 4 million square kilometers per day translates into a staggering 70 terabytes of imagery every day, significantly more data than the rest of the industry combined!